Overview:
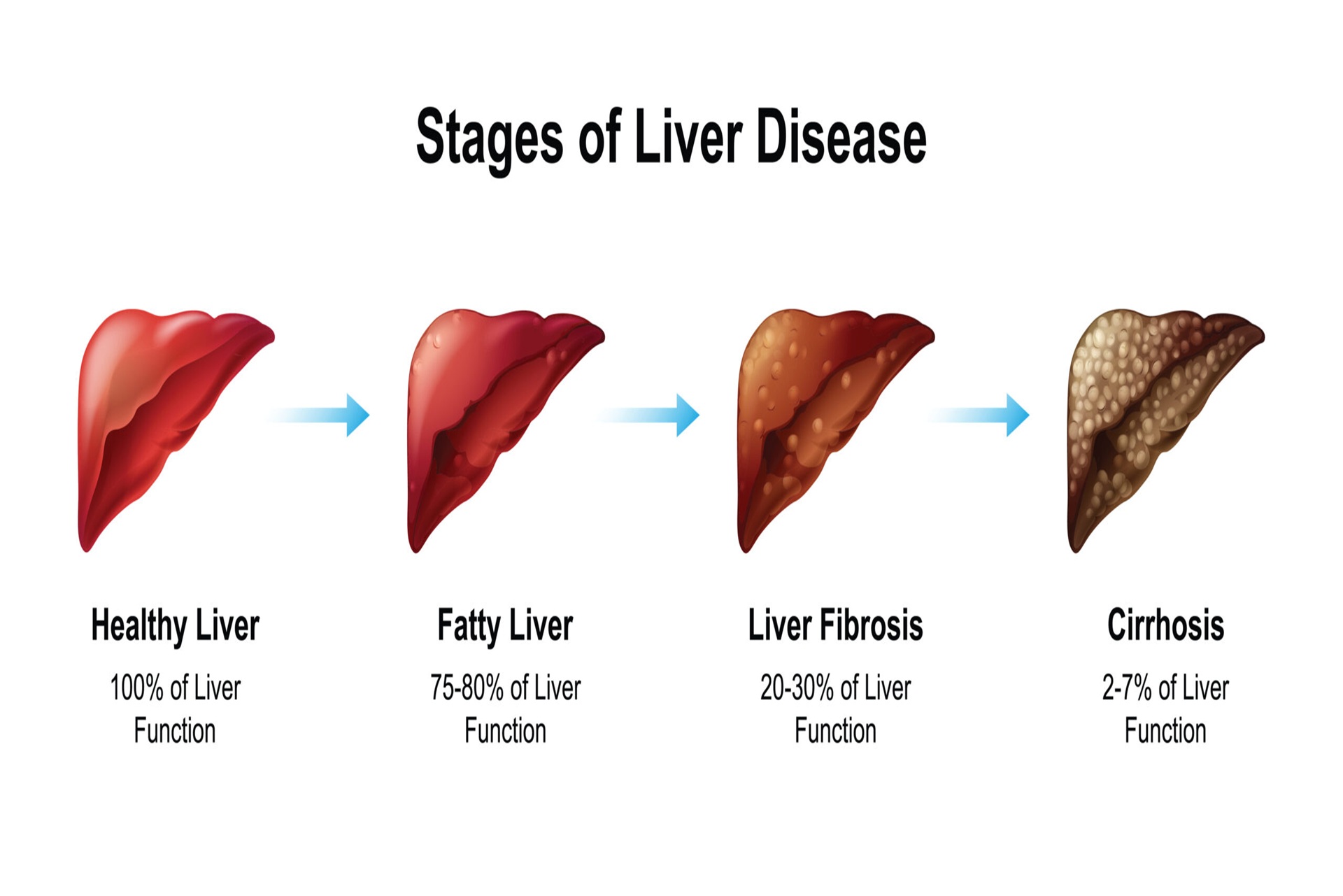
Chronic Liver Disease (CLD) is a progressive condition that leads to long-term liver damage, affecting its ability to function properly. It includes conditions like cirrhosis, fibrosis, and liver failure, which can result in severe complications if left untreated.
Causes:
CLD can be caused by hepatitis B or C infections, excessive alcohol consumption, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), autoimmune liver diseases, genetic disorders, and prolonged exposure to toxins or certain medications.
Symptoms:
Common symptoms of CLD include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), abdominal pain, swelling, fatigue, nausea, loss of appetite, unintended weight loss, and easy bruising. Advanced cases may lead to ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, or variceal bleeding.
Treatment:
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Lifestyle modifications, including a balanced diet, alcohol cessation, and weight management, are crucial. Medications may be prescribed to control symptoms and slow disease progression. In severe cases, liver transplantation may be necessary.
Precautions:
Patients should avoid alcohol, follow a low-sodium diet, take prescribed medications, and get regular liver function tests. Vaccination against hepatitis A and B is recommended.
Prevention:
A healthy lifestyle, limited alcohol consumption, weight management, and early detection of liver conditions can help prevent CLD.
For expert CLD care, visit KDM Hospital in Lucknow, offering ambulance services, budget-friendly care, Ayushman card acceptance, and 24/7 doctor availability.
