Overview:
Dialysis is a medical treatment that replicates the functions of the kidneys in patients whose kidneys are no longer able to adequately filter waste, excess fluids, and toxins from the blood. It is typically used in cases of chronic kidney disease (CKD) or acute kidney failure when the kidneys have lost their ability to function effectively. Dialysis helps maintain the body’s balance of fluids and electrolytes, which is essential for health.
Causes:
Dialysis is required in cases of kidney failure, which can be caused by various conditions, including diabetes, hypertension, glomerulonephritis, polycystic kidney disease, or acute kidney injury. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the leading cause of kidney failure and requires ongoing dialysis treatment.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of kidney failure that may lead to the need for dialysis include swelling, fatigue, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, difficulty concentrating, loss of appetite, and changes in urine output. If untreated, these symptoms can worsen and cause severe complications.
Treatment:
There are two primary types of dialysis: Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis.
- Hemodialysis: A machine filters waste and excess fluid from the blood. It requires access to the bloodstream, typically through a fistula or catheter.
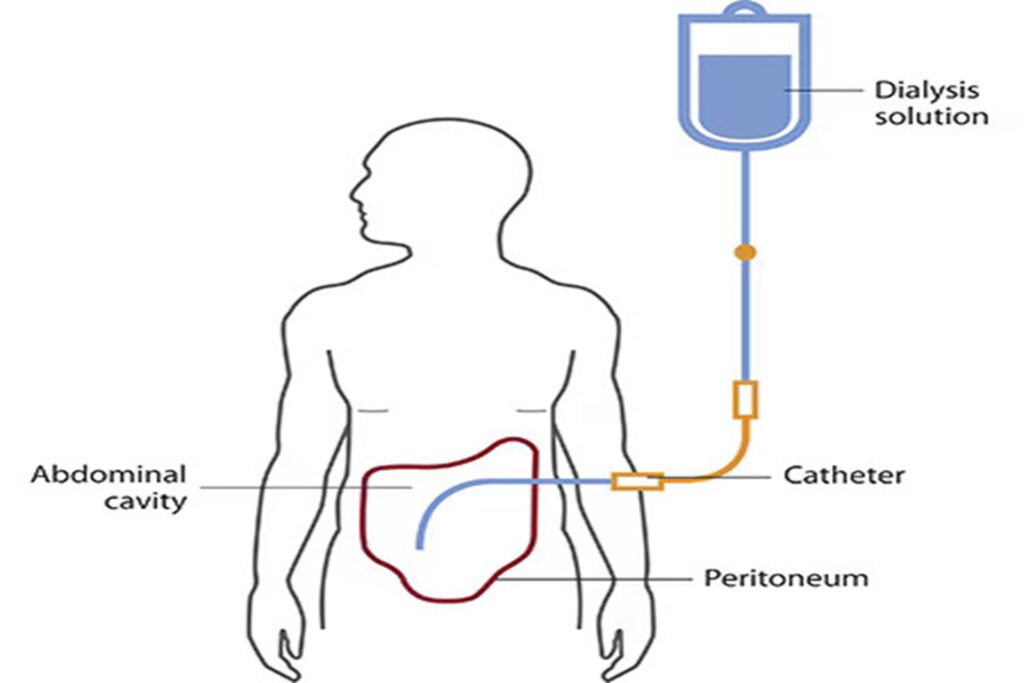
- Peritoneal Dialysis: Uses the lining of the abdomen (peritoneum) to filter blood inside the body with the help of a special fluid, which is infused and drained through a catheter in the abdomen.
Treatment frequency varies depending on the severity of kidney failure, but it is often required several times a week.
Precautions:
Patients undergoing dialysis should adhere to dietary restrictions, such as limiting potassium, phosphorus, and sodium intake. They must also manage fluid intake to prevent excess fluid build-up between sessions. Regular check-ups are essential to monitor for complications such as infection, blood pressure changes, and electrolyte imbalances. Ensuring proper hygiene during dialysis treatments is crucial to prevent infections, especially with peritoneal dialysis.
Prevention:
While dialysis is a treatment for kidney failure, preventing kidney disease is essential. Managing conditions like hypertension and diabetes, maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding smoking, and staying hydrated can help protect kidney function and reduce the risk of kidney failure.
For comprehensive dialysis care, visit KDM Hospital in Lucknow. The hospital provides state-of-the-art dialysis facilities, including both hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, and a team of experienced nephrologists to support patients with kidney-related conditions.
