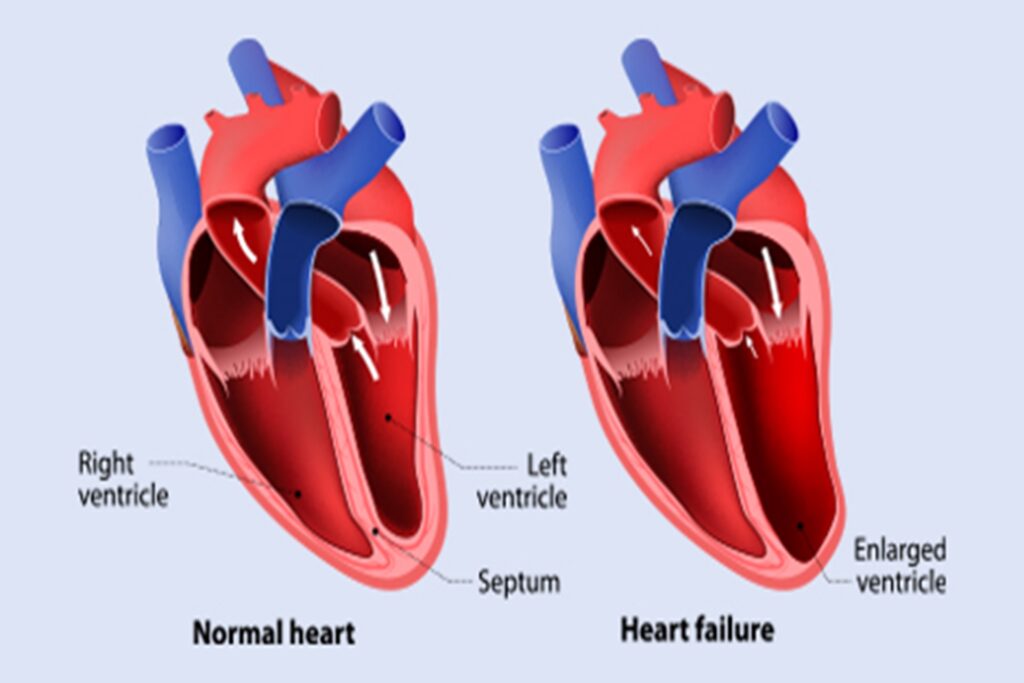
Overview:
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently to meet the body’s needs. It often occurs as a result of weakened heart muscles or damage caused by conditions like coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, or heart attacks. CHF can lead to fluid buildup in the lungs, liver, abdomen, and lower extremities, resulting in a range of symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling.
Causes:
The main causes of CHF include coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, heart valve disease, diabetes, and previous heart attacks. Other factors that contribute to CHF include excessive alcohol consumption, viral infections, and congenital heart defects. Over time, the heart’s inability to pump blood efficiently can lead to CHF.
Symptoms:
Common symptoms of CHF include shortness of breath (especially with physical activity or while lying down), swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet, fatigue, rapid or irregular heartbeat, weight gain due to fluid retention, and difficulty concentrating. In severe cases, patients may experience sudden weight gain and extreme difficulty breathing, indicating a worsening condition.
Treatment:
Treatment for CHF focuses on relieving symptoms, improving heart function, and preventing complications. Common treatments include medications such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics, and aldosterone antagonists. Lifestyle changes such as a low-sodium diet, regular exercise, and weight management are essential. In advanced cases, surgical interventions like heart transplants or left ventricular assist devices (LVAD) may be required.
Precautions:
Patients with CHF should manage underlying health conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and cholesterol levels. Regular monitoring of weight and fluid intake is crucial. Patients should also avoid excessive salt and alcohol consumption, quit smoking, and ensure they’re following the prescribed treatment plan. Adherence to follow-up appointments with a cardiologist is essential for effective management.
Prevention:
Preventing CHF involves managing risk factors such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, and diabetes. Maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and staying physically active can all reduce the risk of developing CHF. Early intervention and regular check-ups can help detect heart disease before it progresses to heart failure.
For expert care in Congestive Heart Failure (CHF), visit the KDM Hospital in Lucknow. The hospital offers advanced heart care, including diagnostic services, treatment for heart failure, 24/7 doctor availability, ambulance services, budget-friendly options, and Ayushman card acceptance.
