Overview:
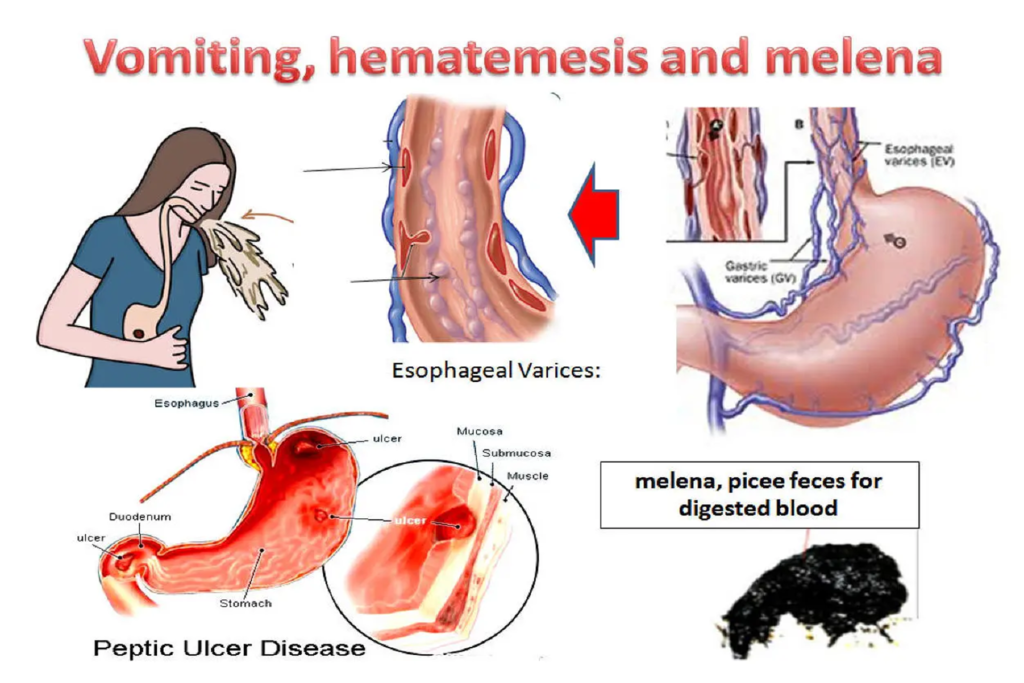
Hematemesis refers to the vomiting of blood, which can range from small amounts to large volumes. This condition is typically a sign of bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. Hematemesis is a serious medical condition and requires immediate attention.
Causes:
The primary causes of hematemesis include gastric ulcers, esophageal varices, bleeding from a tear in the lining of the esophagus (Mallory-Weiss tear), or gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining). Other causes may include liver disease, blood vessel abnormalities, or the use of medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can irritate the stomach lining.
Symptoms:
The most obvious symptom of hematemesis is the presence of blood in vomit. The blood may appear bright red, indicating recent bleeding, or it may look like coffee grounds, which suggests older blood. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, dizziness, weakness, fainting, and a rapid heart rate, especially if the bleeding is significant.
Treatment:
Treatment of hematemesis depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the bleeding. It may include hospitalization for observation, intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration, and blood transfusions if necessary. Medications such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) may be used to reduce stomach acid and promote healing. In more severe cases, endoscopic procedures or surgery may be needed to stop the bleeding.
Precautions:
Patients with a history of gastric ulcers, liver disease, or heavy alcohol use should avoid excessive alcohol consumption, NSAIDs, and smoking, as these can increase the risk of bleeding. Regular check-ups and monitoring for any underlying gastrointestinal conditions are important.
Prevention:
Preventing hematemesis involves managing conditions that cause bleeding, such as controlling ulcers or liver disease, taking medications as prescribed, and avoiding irritants like alcohol and NSAIDs. Maintaining a balanced diet and managing stress levels can also help in reducing the risk.
For expert care in treating hematemesis, visit KDM Hospital in Lucknow. The hospital offers comprehensive services, including 24/7 emergency care, diagnostic facilities, and specialized treatments for gastrointestinal conditions.
