Overview:
Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix, a small, finger-shaped pouch attached to the large intestine. It is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment, as a ruptured appendix can lead to life-threatening complications such as peritonitis or abscess formation.
Causes:
Appendicitis occurs when the appendix becomes blocked, usually due to hardened stool, infection, enlarged lymphoid tissue, or, in rare cases, tumors. The blockage leads to bacterial overgrowth, swelling, and inflammation, which can eventually cause the appendix to rupture.
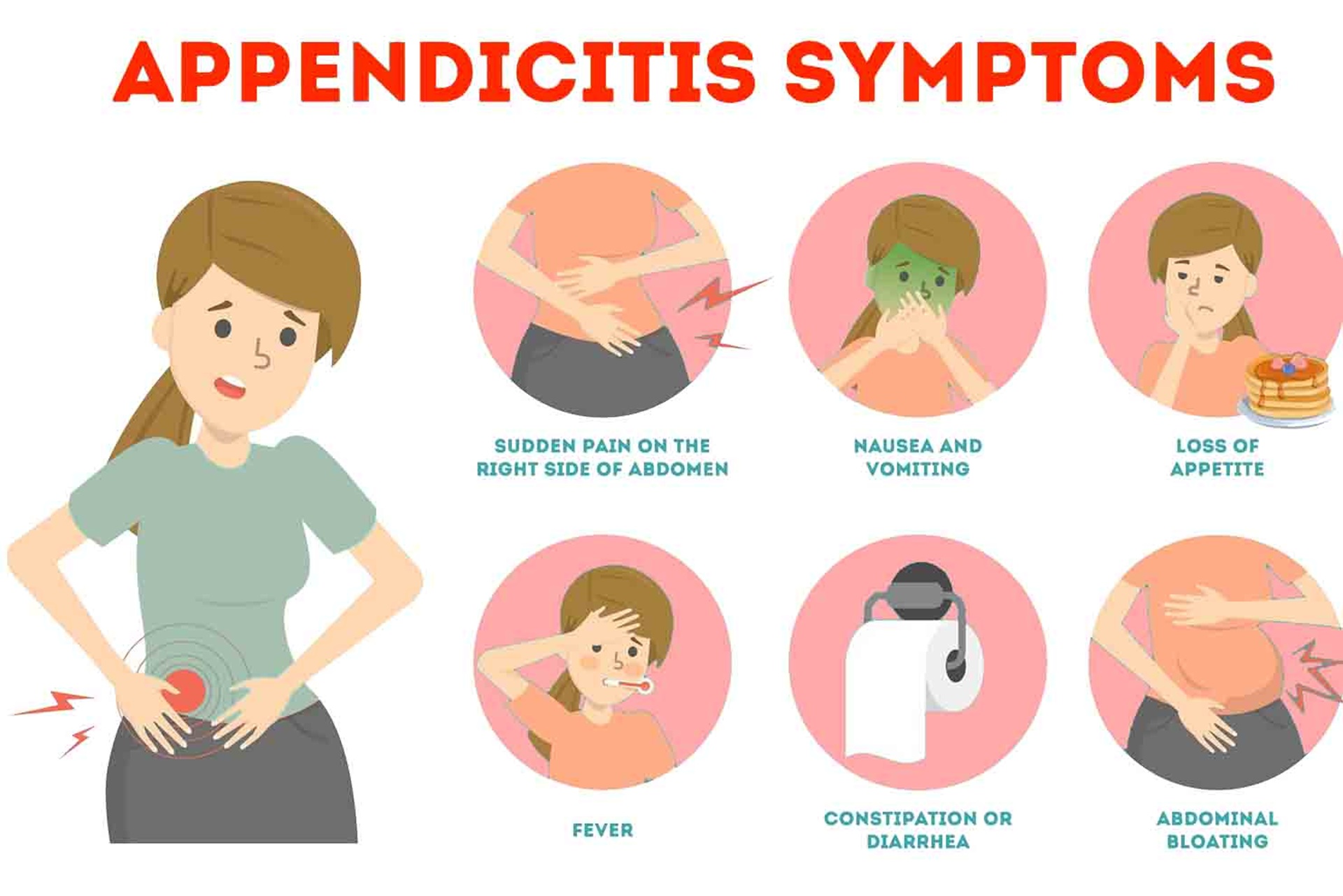
Symptoms:
Common symptoms of appendicitis include sudden and severe pain in the lower right abdomen, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fever, and swelling in the abdomen. Pain may worsen with movement, coughing, or deep breathing. In some cases, symptoms may be mild or atypical, making diagnosis challenging.
Treatment:
The primary treatment for appendicitis is surgical removal of the appendix (appendectomy). This can be done through laparoscopic or open surgery. If an abscess has formed, drainage may be required before surgery. In mild cases, antibiotics may be given to control infection, but surgery remains the definitive treatment.
Precautions:
Patients should seek immediate medical attention if they experience persistent abdominal pain, fever, or digestive issues. Avoid taking pain relievers or laxatives without consulting a doctor, as they can mask symptoms or worsen the condition.
Prevention:
While appendicitis cannot always be prevented, maintaining a healthy diet rich in fiber (fruits, vegetables, and whole grains) may help reduce the risk of blockage and inflammation.
For expert care in appendicitis treatment, visit The KDM Hospital in Lucknow, offering ambulance services, budget-friendly care, Ayushman card acceptance, and 24/7 doctor availability.
