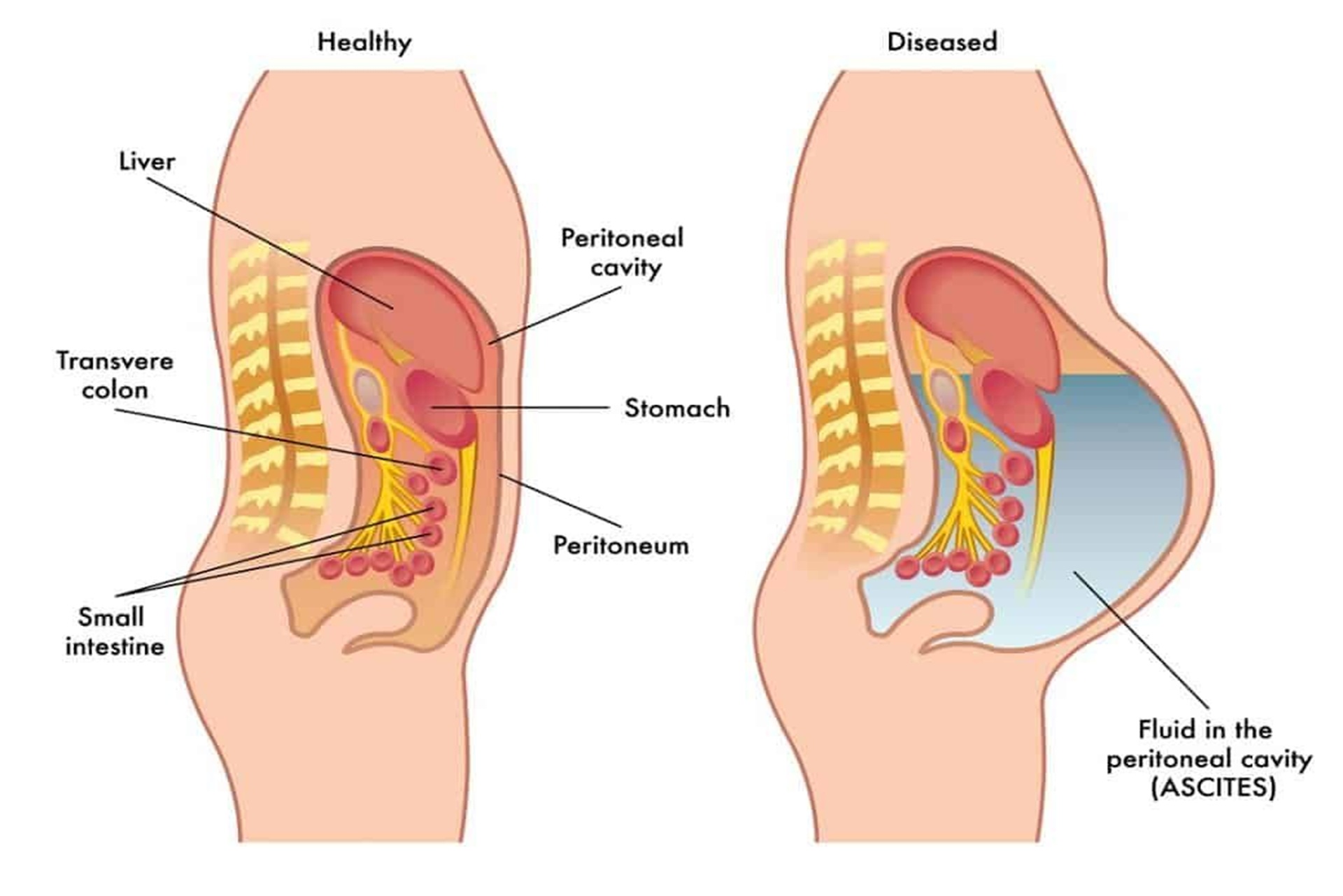
Overview:
Ascites is the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, usually caused by liver disease, cancer, or heart failure. It can lead to discomfort, breathing difficulties, and complications like infections if left untreated.
Causes:
The most common cause of ascites is cirrhosis due to chronic liver disease. Other causes include cancer (peritoneal carcinomatosis), kidney disease, congestive heart failure, and tuberculosis. Portal hypertension (increased pressure in the liver’s blood vessels) plays a major role in fluid buildup.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of ascites include abdominal swelling, weight gain, bloating, shortness of breath, loss of appetite, nausea, and fatigue. Severe cases may lead to an increased risk of infections, kidney dysfunction, or fluid buildup in the lungs.
Treatment:
Treatment focuses on managing the underlying cause. Doctors may recommend a low-sodium diet and diuretics to reduce fluid accumulation. In severe cases, paracentesis (fluid removal via a needle) or a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedure may be necessary.
Precautions:
Patients with ascites should monitor their salt intake, avoid alcohol, and follow their doctor’s advice regarding medications. Regular medical check-ups are essential to prevent complications like spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP).
Prevention:
Preventing liver disease through a healthy diet, controlled alcohol consumption, vaccination against hepatitis, and early treatment of conditions like heart or kidney disease can help reduce the risk of ascites.
For expert care in ascites management, visit The KDM Hospital in Lucknow, offering ambulance services, budget-friendly care, Ayushman card acceptance, and 24/7 doctor availability.
